Javascript State Machine v2
Fri, Aug 19, 2011I have released v2 of my javascript finite state machine, improving the documentation and tests as well as adding a number of new features…
- asynchronous state transitions.
- consistent arguments for all callbacks (event, from, to).
- new generic
onchangestatecallback. - allow callbacks to be declared at creation time.
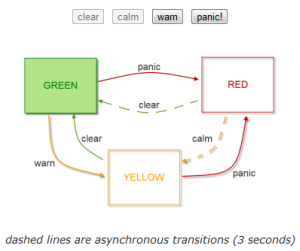
I have updated the demo to include 2 asynchronous transitions that take 3 seconds to complete (watch the output window for the countdown).
The code, as always, available on github.
Asynchronous state transitions
Sometimes, you need to execute some asynchronous code during a state transition and ensure the new state is not entered until your code has completed.
A good example of this is when you transition out of a menu state, perhaps you want to gradually
fade the menu away, or slide it off the screen and don’t want to transition to your game state
until after that animation has been performed.
You can now return false from your onleavestate handler and the state machine
will be ‘put on hold’ until you are ready to trigger the transition using the new transition()
method.
For example, using jQuery effects:
var fsm = StateMachine.create({
initial: 'menu',
events: [
{ name: 'play', from: 'menu', to: 'game' },
{ name: 'quit', from: 'game', to: 'menu' }
],
callbacks: {
onentermenu: function() { $('#menu').show(); },
onentergame: function() { $('#game').show(); },
onleavemenu: function() {
$('#menu').fadeOut('fast', function() {
fsm.transition();
});
return false; // tell StateMachine to defer next state until we call transition (in fadeOut callback above)
},
onleavegame: function() {
$('#game').slideDown('slow', function() {
fsm.transition();
};
return false; // tell StateMachine to defer next state until we call transition (in slideDown callback above)
}
}
});
Callback Changes
(NOTE: in previous versions callbacks were referred to as ‘hooks’)
4 callbacks are available if your state machine has methods using the following naming conventions:
- onbeforeevent - fired before the event
- onleavestate - fired when leaving the old state
- onenterstate - fired when entering the new state
- onafterevent - fired after the event
You can affect the event in 2 ways:
- return
falsefrom anonbeforeeventhandler to cancel the event. - return
falsefrom anonleavestatehandler to perform an asynchronous state transition (see previous section)
For convenience, the 2 most useful callbacks can be shortened:
- onevent - convenience shorthand for onafterevent
- onstate - convenience shorthand for onenterstate
In addition, a generic onchangestate() callback can be used to call a single function for all state changes:
All callbacks will be passed the same arguments:
- event name
- from state
- to state
- (followed by any arguments you passed into the original event method)
Callbacks can be specified when the state machine is first created:
var fsm = StateMachine.create({
initial: 'green',
events: [
{ name: 'warn', from: 'green', to: 'yellow' },
{ name: 'panic', from: 'yellow', to: 'red' },
{ name: 'calm', from: 'red', to: 'yellow' },
{ name: 'clear', from: 'yellow', to: 'green' }
],
callbacks: {
onpanic: function(event, from, to, msg) { alert('panic! ' + msg); },
onclear: function(event, from, to, msg) { alert('thanks to ' + msg); },
ongreen: function(event, from, to) { document.body.className = 'green'; },
onyellow: function(event, from, to) { document.body.className = 'yellow'; },
onred: function(event, from, to) { document.body.className = 'red'; },
}
});
fsm.panic('killer bees');
fsm.clear('sedatives in the honey pots');
...
Additionally, they can be added and removed from the state machine at any time:
fsm.ongreen = null;
fsm.onyellow = null;
fsm.onred = null;
fsm.onchangestate = function(event, from, to) { document.body.className = to; };
Enjoy!
Let me know if you have any problems, or have any feature requests for v3…